TL;DR
-
Many AI code review tools struggle with real projects because they lack enough context
-
Running code reviews locally in the CLI helps catch issues earlier, before a pull request is created
-
This article explains how the Entelligence CLI fits into everyday development and how teams can use it effectively
Introduction
AI code reviews are becoming common as teams look for ways to catch issues earlier and reduce the load on human reviewers. With faster development cycles and more code being written, especially with AI assistance, automated reviews are often seen as a way to scale feedback without slowing teams down.
At the same time, many teams struggle to trust AI code reviews in real repositories. Feedback can feel generic, miss important context, or fail to account for how the codebase has evolved over time, which limits how useful the reviews are in practice.
This article explains where AI code reviews fall short, how running reviews locally in the CLI helps, and how developers can use the Entelligence CLI to review code effectively in real-world projects.
Why AI Code Reviews Often Fail in Practice
AI code reviews can be helpful, but many teams find that the feedback does not hold up once applied to real projects. These failures usually come from limitations in context rather than model capability.
-
Generic feedback with low signal: Comments often restate what the code is doing or suggest broadly applicable best practices without pointing to real issues that matter in the codebase.
-
Hallucinations caused by missing context: When reviews lack repository or dependency context, AI systems may flag problems that do not exist or misunderstand how code is actually used.
-
Shallow reviews focused on syntax: Many reviews focus on formatting or minor style issues instead of examining behavior, edge cases, error handling, or test coverage.
Why Real Codebases Are Harder Than Demos
Most AI code review tools perform well in controlled examples, but real production codebases introduce complexity that is difficult to capture in isolation. These challenges come from how software evolves over time, not from individual code changes alone.
-
Cross-file dependencies
Changes in one file often affect behavior in other parts of the system, making it difficult to review code correctly without understanding related modules and interfaces.
-
Evolving architecture and legacy decisions
Real codebases contain historical patterns, workarounds, and design trade-offs that are not obvious from a single pull request but are critical to correct behavior.
-
Partial diffs without full repository context
Reviewing only the lines that changed can hide assumptions, shared logic, or constraints that exist elsewhere in the repository.
Grounding AI Reviews in Repository Context
Useful AI code reviews depend on understanding more than just the lines that changed. Repository structure provides important context about how code is organized, how components interact, and where shared logic lives. Historical context explains why certain patterns or decisions exist and helps avoid suggestions that conflict with established behavior.
Reviews that focus only on isolated diffs often miss these factors, which leads to inaccurate or low value feedback. Context-aware reviews, by contrast, consider surrounding code, dependencies, and prior changes, resulting in feedback that is more relevant, trustworthy, and easier to act on.
Reviewing Code Locally vs in the Browser
AI code reviews can be delivered through different interfaces, most commonly cloud dashboards or local command line tools. Each approach has strengths, but they fit different stages of the development workflow.
|
Aspect |
Cloud Dashboard–Based Reviews |
Local CLI–Based Reviews |
|---|---|---|
|
When reviews run |
After code is pushed or a pull request is opened |
Before commit, on local staged or unstaged changes |
|
Workflow impact |
Requires switching to a browser or external UI |
Runs in the same terminal used for coding and testing |
|
Feedback timing |
Later in the review cycle |
Early, while code is still being written |
|
Context switching |
Higher, due to dashboard navigation |
Lower, since feedback stays in the CLI |
|
Iteration speed |
Slower feedback loop |
Faster local iteration and re-review |
|
Best use case |
Team level review and collaboration |
Individual developer feedback and early issue detection |
Local CLI reviews fit best early in the development process, where developers want fast, focused feedback without breaking flow. By catching issues before a pull request is created, CLI-based reviews help reduce review noise and make downstream code reviews more efficient.
Introducing the Entelligence CLI
The Entelligence CLI is designed to bring AI-powered code reviews directly into a developer’s local workflow. Instead of waiting for feedback after opening a pull request, developers can review their code while they are still coding, testing, and preparing commits. This shifts code review earlier in the development lifecycle, where issues are easier to fix and less likely to turn into long review discussions.
The CLI fits before the pull request stage and complements existing review processes rather than replacing them. By resolving common issues locally, pull requests stay cleaner and more focused, allowing human reviewers to spend more time on design and intent instead of basic corrections.
-
Local Reviews Before Commit: Review staged and unstaged code changes directly from the terminal to catch bugs, logic errors, missing tests, and problematic AI-generated code early.
-
Feedback Without Context Switching: Trigger reviews and receive actionable, line-level feedback directly in the CLI without leaving the developer’s existing command-line workflow.
-
Context-Aware Code Reviews: Reviews take repository context and dependencies into account, producing more relevant feedback than isolated diff analysis.
-
Cleaner Pull Requests: By resolving issues locally, pull requests contain fewer basic issues, which helps shorten review cycles and reduce noise.
-
Built for AI-Assisted Development: The CLI fits naturally into AI coding workflows by reviewing AI-generated code and flagging hallucinations, logic issues, and missing unit tests.
How the Entelligence CLI Fits Into a Developer Workflow
-
Review staged and unstaged changes locally: Run reviews on code that is still in progress or ready to be committed, without waiting to open a pull request.
-
Catch issues early in the development cycle: Identify bugs, logic errors, missing tests, and AI-generated issues while the code is still being written, when fixes are easier to apply.
-
Iterate quickly in the same environment: Apply feedback, update the code, and re-run reviews directly from the terminal without switching tools.
-
Reduce pull request review noise: Resolve common issues locally so pull request reviews can focus on design, intent, and higher-level feedback.
-
Maintain flow during development: Keep coding, reviewing, and committing within the same CLI workflow to avoid unnecessary context switching.
A Simple Example: Reviewing Code Before Commit
This example shows how a developer can use the Entelligence CLI to review local code changes before opening a pull request. The goal is to catch issues early and fix them while still in the development flow.
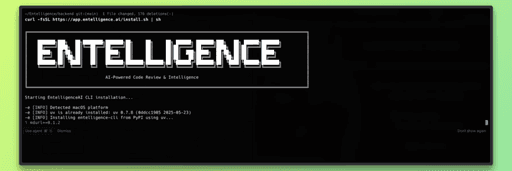
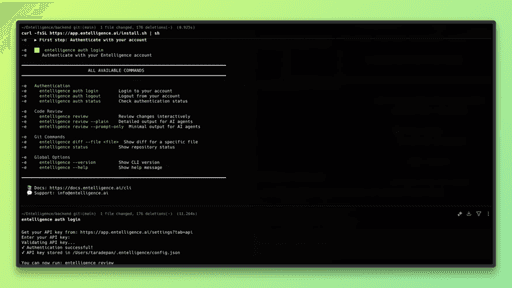
Step 1: Install the Entelligence CLI
Install the CLI using the provided install script. This sets up the entelligence command locally.
Once installed, the CLI is available in your terminal.
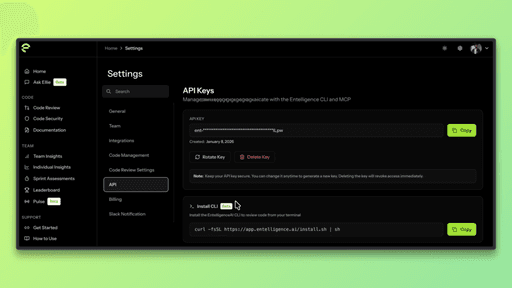
Step 2: Authenticate with Entelligence
To use the CLI, you need to authenticate using your Entelligence account. This typically involves generating an API key from the Entelligence dashboard and logging in through the CLI.
Follow the prompts to authenticate using your API key.
Step 3: Make Code Changes Locally
Edit your code as usual. This can include new features, bug fixes, or AI-generated code. Changes can be staged or unstaged.
For example:
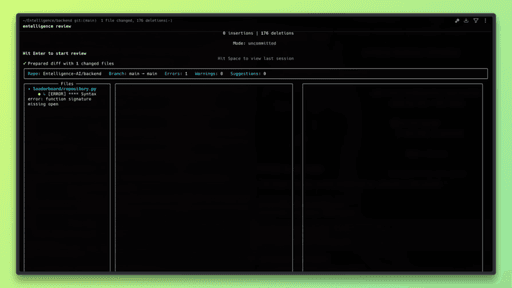
Step 4: Run a Review on Local Changes
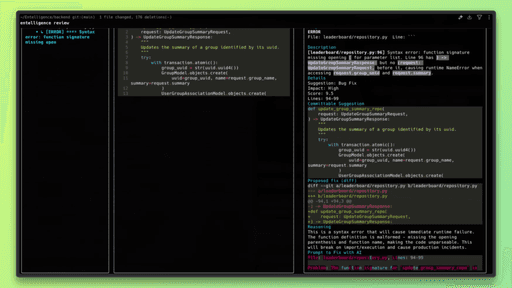
Run the Entelligence review command from the root of your repository. The CLI will analyze the current local changes.
The review runs directly in the terminal and analyzes the modified lines of code.
Step 5: Review Feedback in the Terminal
The CLI prints line-level, actionable feedback directly in the terminal. This can include:
-
Logic or correctness issues
-
Missing tests
-
Code smells or risky patterns
-
Problems in AI-generated code
Developers can fix the issues immediately in their editor.
Step 6: Iterate and Re-Review
After applying fixes, the review can be run again to confirm the changes.
Once the feedback is resolved, the code can be committed and pushed with fewer issues reaching the pull request stage.
Using the CLI in AI-Assisted Development
As AI-assisted coding becomes more common, reviewing generated code before it reaches a pull request is increasingly important. The Entelligence CLI is designed to fit into this workflow by providing local, context-aware reviews for AI-generated changes.
-
Review AI-Generated Code Locally: Run reviews on code produced by AI tools directly in the CLI before committing, using the same local workflow as human-written code.
-
Catch Logical Errors and Missing Tests: Identify hallucinations, incorrect assumptions, missing unit tests, and risky patterns in AI-generated code early in the development cycle.
-
Provide Context-Rich Feedback to AI Tools: Use the review feedback to refine prompts or guide AI coding agents, helping improve subsequent code generation without relying on pull request feedback loops.
Evaluating AI Code Review Quality
These criteria help teams assess whether an AI review tool improves code quality without adding friction to the development process.
-
Why the number of comments is a poor metric: A high volume of comments does not indicate quality. Useful reviews focus on meaningful issues rather than restating obvious or low-impact observations.
-
Signal-to-noise ratio: High-quality reviews surface relevant problems while avoiding unnecessary or repetitive feedback that slows down development.
-
Relevance and correctness of feedback: Review comments should accurately reflect how the code behaves within the repository and avoid suggestions that conflict with existing patterns or constraints.
-
Consistency across similar changes: Reviews should provide stable and predictable feedback when similar issues appear across different parts of the codebase, helping teams build trust in the system.
-
Learning from recurring issues over time: By observing repeated patterns and risks across reviews, the system improves how similar issues are identified in future changes, helping teams reduce recurring problems.
Key Takeaways
-
CLI-based AI code reviews work best when developers want feedback early, before opening a pull request.
-
Individual contributors benefit from local reviews that help catch issues without interrupting their workflow.
-
Teams that iterate quickly can reduce review noise by resolving common issues before code reaches PRs.
-
Projects that rely on AI-assisted coding benefit from local checks that catch logical errors and missing tests early.
-
Using AI reviews in the CLI helps keep pull request discussions focused on design and intent rather than basic fixes.
Use the Entelligence CLI to review code locally and catch issues before they reach a pull request. Explore Entelligence AI to get a unified view of engineering quality, delivery, and team performance across your organization.